Advanced Scaling Configuration - Decision-Making & Auto-Scaling service¶
Overview¶
The Decision Making & Auto-Scaling service allows the user to specify optimization strategies for adapting a cloud application on multiple cloud providers, based on cost, quality and performance preferences. This is achieved by defining elasticity policies for adapting the cloud application both at the design-time of an application and during its runtime execution. There are two ways to define elasticity policies for the Unicorn application: i) via High-level policies that specify an optimization strategy per service; and ii) via Low-level policies that follow an IF-THEN-ACTION approach, where a scaling action is triggered when a set of conditions is satisfied. For this, the Decision Making & Auto-Scaling service continuously monitor these conditions at regular time intervals through application and infrastructure high-level analytic insights.
Features¶
- Define and Manage Elasticity policies for cost, quality and performance optimization of a UNICORN-enabled application
- Autonomous Runtime Monitor & Enforcement of Elasticity policies
- Resource-Aware & Transparent Multi-Cloud Elasticity Control
- Continuous assessment of elasticity policies and adaptation
Components¶
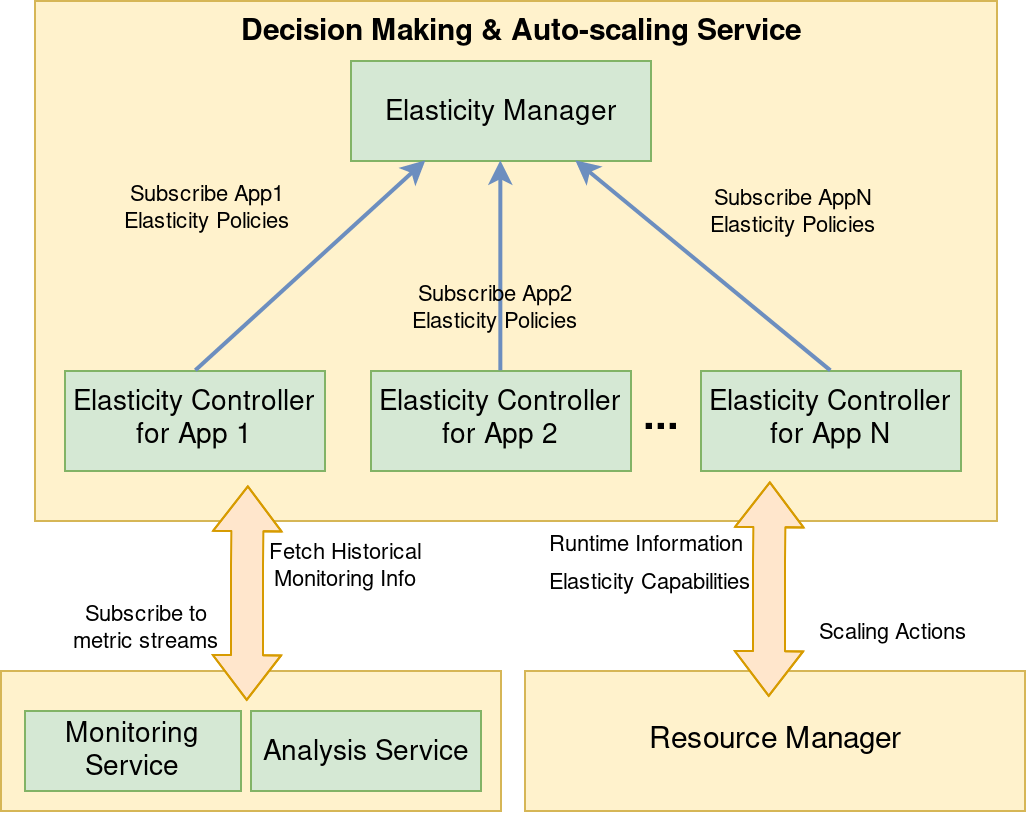
- Elasticity Manager: Allows the user to create, modify and remove elasticity policies
- Elasticity Controller: Enforces the scaling rules of a cloud application
- Analysis Service: Access to real-time analytic metric data
- Monitoring Service: Access to historical monitoring metric data
- Resource Manager: Retrieve elasticity capabilities and propose scaling decisions
Architecture¶
How to use?¶
The elasticity policies can be defined both at the design time of the application through the UNICORN docker-compose file, and during runtime via the service graph of the application.
The following example shows a low-level scale out policy for the streaming_svc service:
scale_out_streaming_svc =
WHEN
average_requests_5m > 100
AND
average_cpu_5m > 80
THEN
SCALE OUT ( 1 service_streaming WITH 30 SECONDS COOLDOWN)
The first part (WHEN) contains two conditions. These conditions specify that
the average_requests_5m must be greater than 100, while also the average_cpu_5m
must exceed 80(%) in order to trigger the scaling action. The action (specified in THEN part),
designates that 1 more service_streaming service should be provisioned.
Note that the WITH 30 SECONDS COOLDOWN is a configurable time period which is used to give time to the system to
provision/de-provision new resources and absorb any changes, in order to prevent false scaling alerts.
Elasticity Policy¶
An elasticity policy can be constructed in two different ways. The first way is the high-level policy which allows the user to specify for a given service of the UNICORN Service Graph, a high-level optimization strategy. Currently, the language supports three optimization strategies per service:
- Cost optimization
- Availability optimization
- Balance between cost and availability
Note that the default strategy is enabled when users do not specify the Awareness construct.
elasticity_streaming_svc =
SET SERVICE streaming_svc AWARE ON COST USING avg_cpu_streaming_utilization
The above segment, shows an example of a high-level elasticity policy. The policy specifies that the service streaming_svc from the UNICORN Service graph should be aware on cost using the average CPU utilization of that service. It is important to mention that the analytic insight avg_cpu_streaming_utilization must have the following properties:
- Indicate the current workload of a service.
- Its value should be decreased when applying a scaling out action, i.e., add more service instances.
- Its value should be increased when applying a scaling in action, i.e., remove service instances.
The second way to define elasticity policies is to construct a low-level policy. This feature is recommended for advanced users as they can express policies with a higher degree of detail. This policy is composed from a set of conditions and a scaling action. Each condition contains an expression of an analytic insight (left hand-side) and a number (right hand-side) which are operated by a binary operation (e.g., <,>,==).
Enablers¶
The Decision-Making and Auto-Scaling service offers to users the ability to activate various optimization modules, namely Enablers. Currently, UNICORN supports the following two enablers:
- UNICORN Predictor
- UNICORN Decision Timeframe Sensitivity
UNICORN Predictor¶
This enabler predicts the values of the analytic insights specified in the ElasticityTrigger construct. The segment below shows how the enabler is activated. The horizon parameter specifies how far to predict the values (5 minutes), the confidence specifies the maximum acceptable error (95%), and the history parameter denotes how far in the past historic points are considered (2 weeks).
predicted_scale_out =
WHEN avg_cpu_streaming_utilization > 80
ENABLE (UNICORN_PREDICTOR[horizon=300, confidence=0.95, history=10080])
PERFORM SCALE OUT ( 1 streaming_svc WITH 5 MINUTES COOLDOWN)
UNICORN Decision Timeframe Sensitivity¶
This enabler can be activated as shown in the segment below, to enable the dynamic change of the decision timeframe. The Decision timeframe is the time period of the aggregation function used in the analytic insight (avg_cpu_streaming_utilization). It uses a confidence value, with higher values resulting to larger time periods. The benefit of this approach is that the user doesn’t need to manually find and set the aggregation period of the metric streams used for scaling decisions.
sensitivity_scale_out =
WHEN avg_cpu_streaming_utilization > 80
ENABLE (UNICORN_SENSITIVITY[confidence=0.95])
PERFORM SCALE OUT ( 1 streaming_svc WITH 5 MINUTES COOLDOWN)
Available Actions¶
Currently two actions are supported for horizontal scalability.
The SCALE OUT action, which provisions a new instance of a service and the
SCALE IN action, that de-provisions an existing instance of a service.
Elasticity Grammar¶
The Table below presents the Elasticity languagre grammar rules in EBNF syntax.
| ElasticityPolicy | ::= |
|
| ElasticityPolicyID | ::= | <String> |
| HighLevelPolicy | ::= | “SET” <Service> [ <Awareness> ] “USING” <InsightID> |
| Service | ::= | <GraphID> “:” <GraphInstanceID> “:” <ServiceID> |
| Awareness | ::= | “AWARE ON” <Strategy> |
| Strategy | ::= | “COST” | “AVAILABILITY” |
| LowLevelPolicy | ::= | “WHEN” <ElasticityTrigger> [<Enablers>] “PERFORM” <ElasticityAction> |
| ElasticityTrigger | ::= | <ElasticityCondition> ( “AND” <ElasticityCondition> )* |
| ElasticityCondition | ::= | <InsightID> RelOp <Number> ) |
| Enablers | ::= | “ENABLE” “(” <Enabler> (“,” <Enabler>)* “)” |
| Enabler | ::= | <EnablerName> “[” <Parameters>”]” |
| EnablerName | ::= | <String> |
| Parameters | ::= | <KeyValue> ( “,” <KeyValue> ) |
| KeyValue | ::= | <String> “=” <String> |
| ElasticityAction | ::= | <ReplicationAction> | <InformationAction> |
| ReplicationAction | ::= | ( “SCALE OUT” | “SCALE IN”) <PlacementConfig> |
| PlacementConfig | ::= | “(” <PositiveInt> <Resource> <Cooldown> “)” |
| PositiveInt | ::= | [1-9]([0-9])* |
| Resource | ::= | <Service> | <Service> IN <Cluster> |
| Cluster | ::= | <String> |
| Cooldown | ::= | <PositiveInt> <TimeUnit> “COOLDOWN” |
| TimeUnit | ::= | “MILLISECONDS” | “SECONDS” | “MINUTES” | “HOURS” |